« User Manual 3.3 Spheroids » : différence entre les versions
Page créée avec « ==== Definition ==== A spheroid, or ellipsoid of revolution is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellip... » |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| Ligne 11 : | Ligne 11 : | ||
==== Implementation ==== | ==== Implementation ==== | ||
The Spheroid object in the SIRIUS library implements the [ | The Spheroid object in the SIRIUS library implements the [[User Manual 3.3 The Ellipsoid Interface|Ellipsoid interface]]. Please refer to the [{{JavaDoc3.3}}/org/apache/commons/math3/geometry/euclidean/threed/Spheroid.html Javadoc] for a complete list of public methods. | ||
==== Instantiation ==== | ==== Instantiation ==== | ||
Dernière version du 4 avril 2018 à 14:13
Definition
A spheroid, or ellipsoid of revolution is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal equatorial radii. Assuming the XYZ coordinate system is such that the spheroid is centered and axis-aligned, the spheroids equation is given by:
The equatorial radius is called the transverse radius whereas the polar radius [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] is the conjugate radius.
Implementation
The Spheroid object in the SIRIUS library implements the Ellipsoid interface. Please refer to the Javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
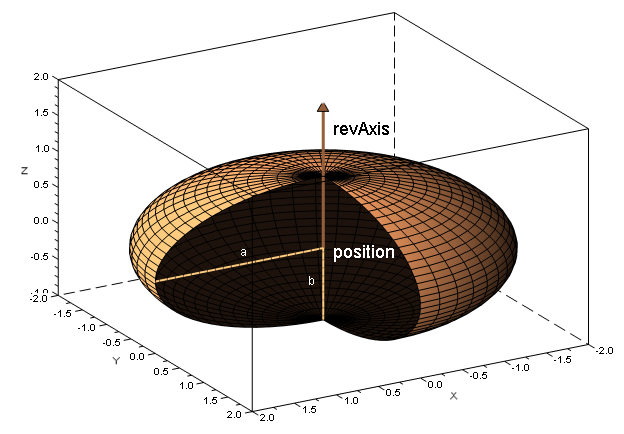
In order to instantiate a spheroid object, the user must specify the spheroids' center, it's axis of revolution and both semi-axis (the transverse radius [math]\displaystyle{ a }[/math] and the conjugate radius [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math]). For example :
// Spheroid parameters
Vector3D position = new Vector3D(1, 2, 3);
Vector3D revAxis = new Vector3D(0, 1, 1);
double a = 2.0;
double b = 1.0;
// The spheroid itself
Spheroid mySpheroid = new Spheroid(position, revAxis, a, b);
Usage
Please refer to the [MAT_GEO_Home#HInteractions Interactions with other geometrical objects section] for methods inherited from the Shape interface.